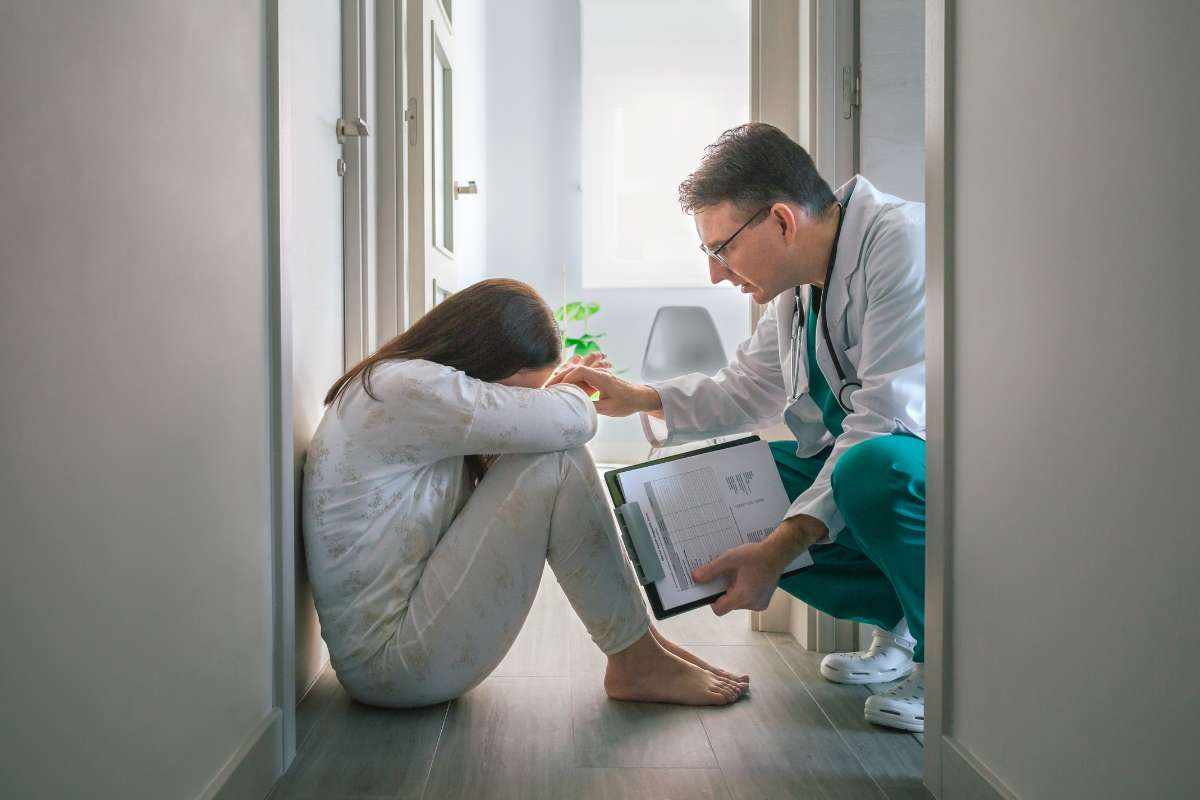
Introduction to Abnormal Psychology
Abnormal psychology is a branch of psychology that focuses on the study of atypical patterns of behavior, emotion, and thought. It delves into understanding and treating mental disorders, offering insights into the complexities of the human mind. The significance of abnormal psychology lies in its contribution to improving the lives of individuals affected by psychological disorders and enhancing our understanding of human behavior.
Historical Perspectives
Throughout history, diverse cultures have interpreted and responded to abnormal behavior in various ways. Early civilizations attributed mental illness to supernatural forces, resorting to rituals and exorcisms as treatments. It wasn’t until the Renaissance that more humane approaches, such as moral treatment, emerged. The 20th century witnessed significant advancements in psychological understanding, paving the way for modern diagnostic and therapeutic practices.
Theoretical Approaches
Abnormal psychology adopts multiple theoretical frameworks to elucidate the causes and manifestations of mental disorders. The biological perspective emphasizes genetic, neurochemical, and neuroanatomical factors contributing to abnormal behavior. Psychodynamic theories explore unconscious conflicts and early life experiences, while behavioral models focus on observable behaviors and learning processes. Cognitive perspectives examine distorted thought patterns, while sociocultural approaches consider the influence of cultural norms and social contexts on mental health.
Common Mental Disorders
Anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and phobias, are characterized by excessive fear and worry. Mood disorders encompass depression and bipolar disorder, marked by disturbances in mood regulation. Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders involve disruptions in perception, cognition, and social functioning. Personality disorders are characterized by rigid and maladaptive personality traits, leading to interpersonal difficulties. Substance-related and addictive disorders involve compulsive substance use despite negative consequences.
Etiology of Abnormal Behavior
The etiology of mental disorders is multifaceted, involving interactions between biological, psychological, and environmental factors. Genetic predispositions, neurochemical imbalances, and structural brain abnormalities contribute to biological vulnerabilities. Psychological factors, such as maladaptive coping mechanisms and unresolved conflicts, can exacerbate symptoms. Environmental stressors, including trauma, abuse, and socioeconomic disadvantage, also play a crucial role in the development of mental illness.
Diagnosis and Assessment
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) and the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) provide standardized criteria for diagnosing mental disorders. Assessment methods encompass clinical interviews, psychological tests, and behavioral observations, facilitating accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Treatment Modalities
Treatment approaches for mental disorders encompass psychotherapy, pharmacotherapy, and adjunctive interventions. Psychotherapy, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, psychodynamic therapy, and interpersonal therapy, aims to alleviate symptoms and improve coping skills. Pharmacotherapy involves the use of psychotropic medications to regulate mood, cognition, and behavior. Other interventions, such as electroconvulsive therapy and transcranial magnetic stimulation, may be utilized in refractory cases.
Stigma and Social Implications
Despite advances in understanding mental illness, stigma remains a pervasive barrier to treatment and recovery. Individuals with mental disorders often face discrimination and social ostracism, hindering their access to healthcare and social support. Efforts to combat stigma and raise awareness about mental health are essential for promoting inclusivity and fostering a supportive community.
Cultural Considerations
Culture plays a significant role in shaping the expression and perception of mental illness. Cultural factors influence symptom presentation, help-seeking behaviors, and treatment preferences. Mental health professionals must be culturally competent, recognizing and respecting the diversity of beliefs and practices across different cultural contexts.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research in abnormal psychology encompasses diverse areas, including neuroscience, genetics, and psychopharmacology. Advances in technology, such as neuroimaging and genetic sequencing, offer new insights into the biological underpinnings of mental disorders. Emerging treatments, such as ketamine-assisted therapy and virtual reality exposure therapy, hold promise for enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
Case Studies and Real-life Examples
Case studies provide valuable illustrations of abnormal behavior and treatment interventions. From schizophrenia to obsessive-compulsive disorder, real-life examples highlight the complexities of mental illness and the efficacy of various treatment modalities. By examining individual cases, clinicians gain insights into diagnostic challenges, treatment strategies, and recovery trajectories.
Ethical Issues in Abnormal Psychology
Ethical considerations are paramount in the practice of abnormal psychology, ensuring the welfare and rights of clients. Confidentiality safeguards client privacy, while informed consent promotes autonomy and decision-making capacity. Maintaining professional boundaries and avoiding dual relationships are essential for preserving the therapeutic alliance and minimizing potential conflicts of interest.
Career Opportunities
Abnormal psychology offers diverse career pathways, including clinical practice, research, and academia. Clinical psychologists, psychiatrists, and psychiatric nurses provide direct care to individuals with mental disorders, utilizing evidence-based interventions. Researchers investigate the underlying mechanisms of abnormal behavior and develop innovative treatments to improve patient outcomes. Educators and academic scholars disseminate knowledge through teaching and scholarly inquiry, shaping the future generation of mental health professionals.
Future Directions
As our understanding of abnormal psychology continues to evolve, new challenges and opportunities arise. Addressing disparities in access to mental healthcare, advancing personalized medicine approaches, and integrating technology into treatment delivery are key priorities. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and embracing innovation, we can strive towards a more comprehensive and compassionate approach to mental health care.
Conclusion
Abnormal psychology encompasses a vast and dynamic field of study, offering invaluable insights into the complexities of human behavior and mental health. From historical perspectives to contemporary research, the exploration of abnormal psychology enriches our understanding of the human condition and informs evidence-based practices. By embracing diversity, challenging stigma, and promoting holistic wellness, we can foster resilience and recovery for individuals affected by mental illness.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What is abnormal psychology? Abnormal psychology is the branch of psychology that focuses on understanding and treating atypical patterns of behavior, emotion and thought associated with mental disorders.
- What are some common mental disorders studied in abnormal psychology? Common mental disorders include anxiety disorders, mood disorders, schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders, personality disorders, and substance-related and addictive disorders.
- What factors contribute to the development of mental disorders? Mental disorders arise from a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and environmental factors, including genetic predispositions, neurochemical imbalances, psychological stressors, and adverse life experiences.
- How are mental disorders diagnosed and treated? Mental disorders are diagnosed using standardized criteria outlined in diagnostic manuals such as the DSM-5 and ICD-10. Treatment modalities encompass psychotherapy, pharmacotherapy, and other interventions tailored to individual needs.
- What are some career opportunities in abnormal psychology? Career opportunities in abnormal psychology include roles in clinical practice, research, academia, and advocacy. Professionals may work as clinical psychologists, psychiatrists, researchers, educators, or mental health advocates, contributing to the advancement of mental healthcare.
References:
- American Psychological Association (APA): The APA website provides a wealth of information, research articles, news, and resources covering various branches of psychology. It’s a go-to source for psychologists, students, and the general public interested in psychology.
- Psychologyorg: Psychologyorg offers a broad range of articles, blogs, and resources covering diverse topics in psychology, mental health, therapy, and self-improvement. It provides insights from psychologists, therapists, and experts in the field.
- Verywell Mind: Verywell Mind is a popular resource that covers mental health and psychology-related topics. It provides comprehensive, evidence-based articles, guides, and expert insights for understanding various psychological conditions and topics.
- MindTools: Focusing on personal and professional development, MindTools offers resources, articles, and tools related to leadership, management, decision-making, and various psychological aspects of personal growth.